Facts about Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Posted by Admin / in Science Facts
A light emitting diode (LED) is designed to light up in a DC (direct current) circuit. In a DC circuit, a LED converts electric current directly into light. LEDs as a light source are one of the most efficient ways to make safe light currently known. The LED is much more efficient than an incandescent light bulb or a fluorescent light bulb (also known as a mercury vapor bulb), which give off more heat, wasting energy.
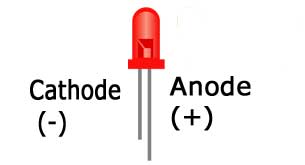
LED anode leg and cathode leg
Facts about LEDs
- LED stands for "Light Emitting Diode"
- A LED lights up by using a small semiconductor crystal. When the crystal is energized with electrical current, the semiconductor emits light.
- The LED semiconductor has n-type (negative) and p-type (positive) material. These two materials give the LED the ability to light up. When current is allowed to flow from the p-type material to the n-type material, the LED emits light.
- A small reflector (like the reflector surrounding a car headlight lamp) surrounds the semiconductor crystal, making the LED brighter.
- An epoxy case surrounds the LED circuit, providing a defined color and protection of the circuit.
- A LED has two legs that are used to connect it into a circuit. The legs, called leads, also help pull heat away from the LED circuit.
- The legs of the LED are not the same. One leg is longer than the other. The longer LED leg is known as the anode. The shorter LED leg is known as the cathode.
- The anode leg helps direct current from the p-type material to the cathode. The anode leg is connected in a circuit towards the positive terminal of the battery. If the LED is connected backwards it will not light up.
- All LEDs are made with a maximum voltage they can connect to without being destroyed. This voltage is typically between 1.5 volts and 3.6 volts. Voltages higher than labeled on the LED packaging will result in a LED that is destroyed.
- Last much longer than traditional light bulbs, but they will fade over time. An LED is no longer considered useful when it has lost 30 percent of its brightness.
- Light bulb makers have developed a way to make a standard light bulb that uses LEDs for its light source.
- LED light bulbs are currently more expensive than traditional light bulbs, but the cost has been reduced by 90 percent over the last several years.
- Natural white LEDs are not available. Instead, light bulb makers mix several different LED bulbs which results in light we see as white.
- The first patent for LEDs was issued to James Biard and Gary Pittman while working at Texas Instrument in 1961.

LEDs are now made to replace incandescent light bulbs
Electrical schematic symbol for a LED
