Facts about Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate)
Posted by Admin / in Science Facts

The White Sands Memorial Dunes in New Mexico is gypsum sand.
These facts about gypsum include them chemistry of gypsum, how gypsum is used, and some history about gypsum. Gypsum is known in chemistry as calcium sulfate dihydrate. It is a very useful material. Learn some important facts about gypsum including where it is found.
Gypsum Facts
- Gypsum is also known as calcium sulfate dihydrate in chemistry or hydrated calcium sulfate.
- The chemical formula for pure gypsum is Ca(SO4)•2(H2O).
- In nature, gypsum is the type of rock that is formed by a chemical process. Gypsum forms crystals, if given the resources and space for formation.
- Gypsum has a unique property. When gypsum is exposed to heat, it releases water. This is one of the reasons that people use drywall (sheetrock) in homes and buildings. Natural or synthetic gypsum is used to make drywall. Not only is gypsum inorganic so it does not easily burn like wood, it has the added fire protection benefit of releasing some water. Standard drywall offers 1/2 hour of protection against fire. Enhanced fire-proof drywall that is thicker and contains fibers to keep the drywall together , offers 1 hour of fire protection.
- In it natural form gypsum looks like rock, but it is soft rock that can be easily scratched.
- Gypsum is soluble in water. Exposure to water over a time period with soften gypsum so it is no longer a solid. Gypsum is about 10 times more soluble in water than limestone.
- Gypsum can be found more than 100 feet below the ground or in some cases at the ground surface.
- Large gypsum crystals have been discovered in the Naica Mine in Chihuahua, Mexico. This cave contains long free-standing gypsum crystals that are 36 feet (12 meters) in length.
- A large gypsum desert is located in New Mexico. Now known as White Sands National Monument operated by the U.S. National Park Service, the gypsum sand dune desert is 275 square miles (over 710 square km) in size.
- Areas around gypsum deposits often have problems with caves and sinkholes. The Carlsbad Cavern in New Mexico is an example of a cavern system make by water dissolving the gypsum over time.

This gypsum mine is found at the ground surface near the Northern coast of the Greek Island of Crete.


How Gypsum is Used
- Natural gypsum was used for many years to make drywall board (sheet rock board). Drywall is used in most residential houses and many commercial buildings in North America and in other countries. Today as mining gypsum becomes more difficult, synthetic gypsum is now used for this purpose.
- Gypsum is used to make Portland Cement. Portland cement is the bonding material that makes concrete so strong. Gypsum is used once the cement is ground into fine powder, gypsum is added to keep the Portland cement from hardening.
- Gypsum is used to make plaster of Paris, which is has many uses such as plaster board walls, decorative plaster molding in houses and buildings, and in artwork.
- Gypsum is used to make plaster for sculpture. The gypsum is great for sculpting because it does not shrink as much as other types of plaster when it hardens. It is also very rigid so it holds up well when using gypsum to make a mold.
- Gypsum is used in farming and landscaping to change the properties of the soil.
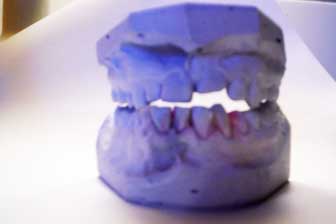
- Gypsum is used by dentists to make molds of teeth. It is also used by people who make special effects for movies props.
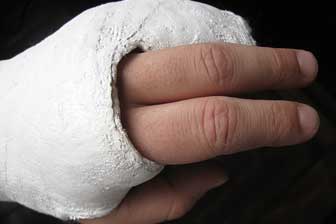
- Gypsum is used in plaster to make a cast to help set and heal broken bones.

Resources:
Naica Giant Crystal Mine Documentation in Mexico
